This essay will be an overlook of the disease that has reached out to one third of the world's population and affected millions of people; some relevant to the media-attracted ear include Niels Abel and Edward Baker Lincoln son of Abraham Lincoln.
Tuberculess bacillus or Tuberclosis or TB was once known as "consumption" as literally one's body will be consumed by the bacteria which cause this disease. The main cause of TB is a bacteria from the myobacterium family. The bacteria enters the body through inhaling infected air and therefore enters the body through the gate of the Respiratory System. When these bacteria have entered the lungs they can multiply and cause a local inflamation or infection which is known as pnemonia.
The body will respond to this unwanted guest by isolating the bacteria and not allowing them to spread throughout the body. The immune system does this by forming scar tissue in a process known as fibrosis around the bacteria to bloak the passages. These scar tissues may harden over time due to calcification of the tissue by the calcium floating in the blood stream. This state of the disease is called Primary or in-active TB. People with in-active tuberculosis, will not experience the range of symptoms experienced by those suffering active TB and will also not be infectious- meaning cannot distribute the disease.
But this natural immunization won't hold back the myobacterium forever. If the immune system of the body weakens due to cancer, other clinical diseases, drugs capable of affecting the immune system such as medications for arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, the bacteria will break free and spread around the body. This is a much more vast and effective operation as the immune system is literaly switched off. This state of the disease is called active TB. Some symptoms of this active state of tuberculosis include night sweats, weakness, tiredness, weightloss and fever. If the inflamation and infection in the lungs becomes more severe, coughing, chest pain, coughing up sputum (matter emmited from the lungs) or even blood as well as shortness of breath can be experienced. If the bacteria spread to other organs of the body, depending on the specific organ being attacked, further symptoms may unveil.
Now that we have talked about the different types of tuberculosis, their source and symptoms, let's have a glance at how TB can be prevented, distinguished and treated.

It is important to know that 8 million people are added to the long list of the "TB affected" anually. It is estimated that about 10-15 million people are suffering TB just in the U.S. The only way this disease can be passed on is via air particle transmition. Of course there are a few factors that can increase the vulnerability of a person in regards with TB. Some of these factors may include alcohol and drug intake, poor immune system, diabetics, those with AIDS, and also some races. Unlike AIDS which is transmitted via contact, TB is transmitted only if infected air particles are inhaled. And because noone is aware of the clinical situation of all the surounding people and noone can detect if the atmosphere is TB infected or not, anyone can fall in the footpath of TB.
But the search for vaccines had started as early as the early 19th century and even untill now, many countries use the BCG vaccination programme when a child is born. The BCG aids the body very weakly in terms of TB and although it can prevent minor damage, it is not a reliable programme. But studies are taking place and new and much more effective vaccines are on the verge of flowing through the body of the public; such as the MVA85A.
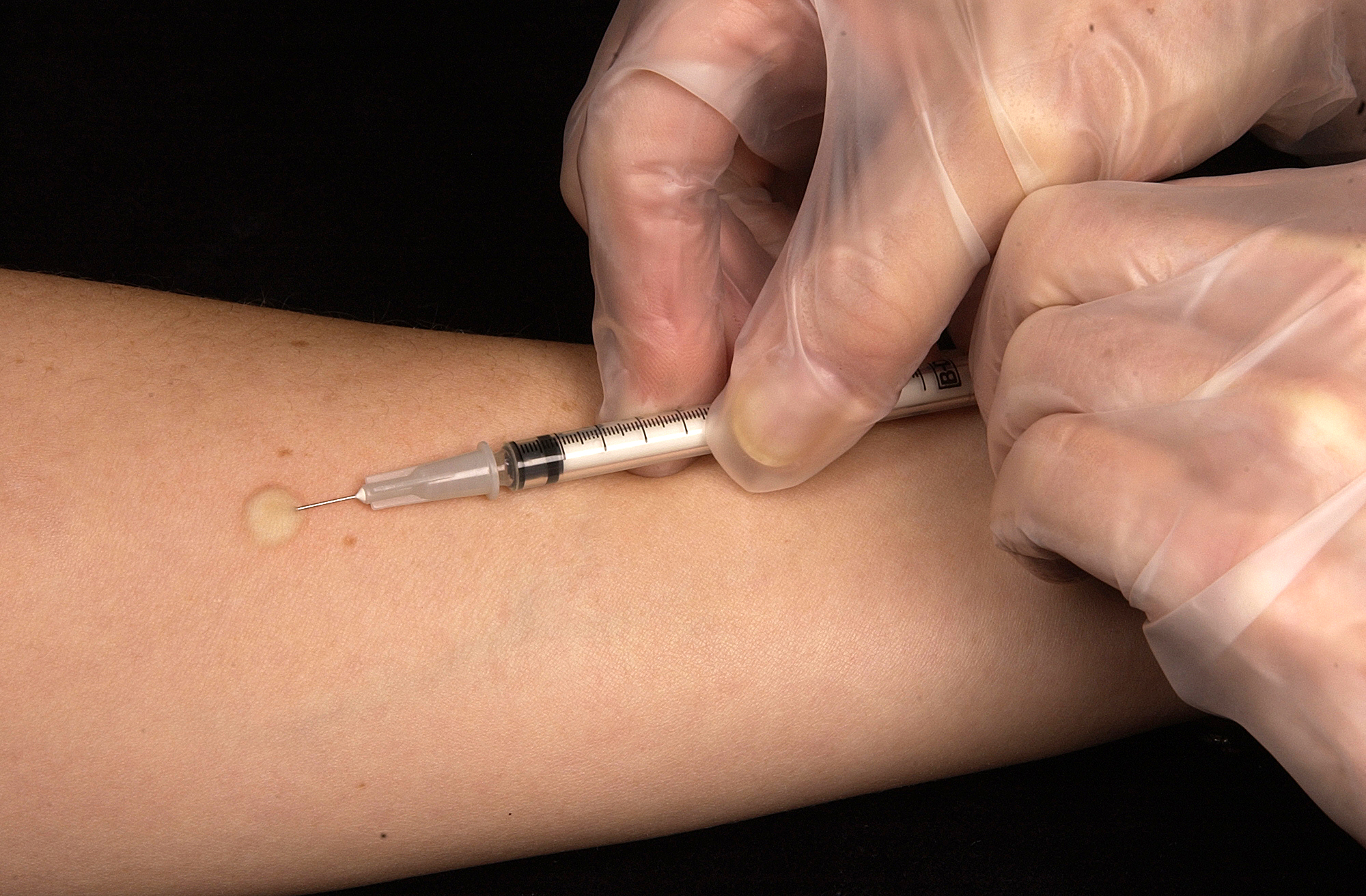
TB is caused by a bacteria and if diagnosed on time, can be dealt with by using antibiotics over a stretched period of time. If any of the symptoms above take place or you just want to make sure you are free of this disease, a skin test can be taken. A fluid - tubercullin - is injected into the skin of the forearm and after 2 or 3 days the amount of swelling around the area is examined. Further examinations will involve X-ray images that will show exactly where the bacteria have attacked and if the TB is at an active or in-active state.


No comments:
Post a Comment